Physical Sciences
Penn State Astronomers Discover Well-Established Black Holes in Distant Quasars
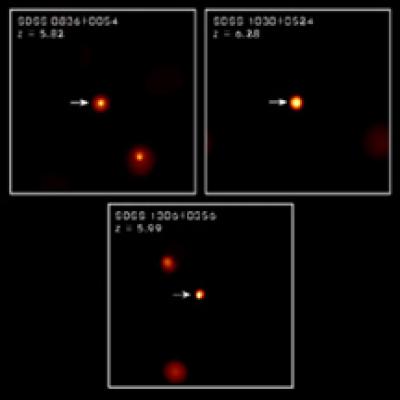

Image

Planets of the Phoenix: Astronomers Predict Rebirth of Planetary Systems in the Embers of Dead Stars
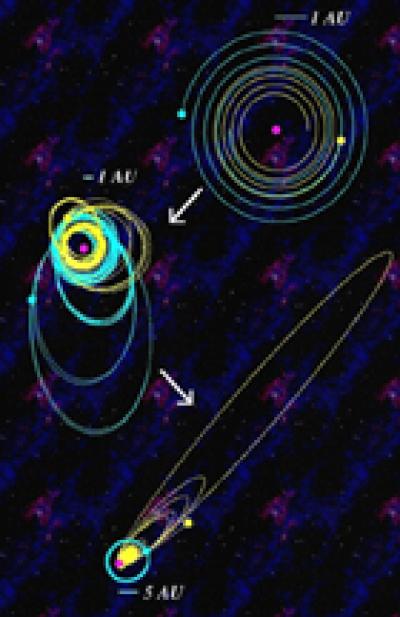
Image

Penn State a Partner in New Global Data Grid
In Powerful Gamma-Ray Bursts, Neutrinos May Fly Out First, Scientists Say
X-ray Emissions Detected from Elusive Cosmic Object
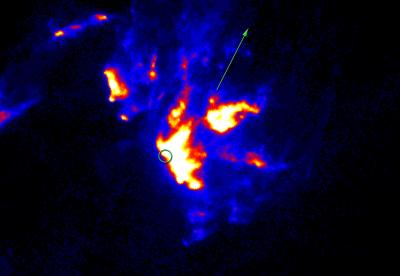
Image

Penn State and SurroMed Describe Submicrometer-Scale Metallic Barcodes
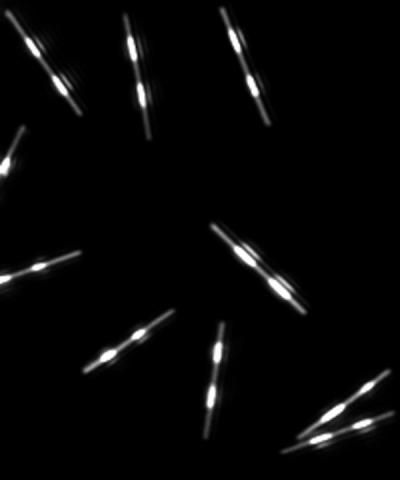

Image

New Center for Gravitational Wave Physics Established at Penn State
Supercomputer Simulations Reveal Strongest Carbon Nanotubes
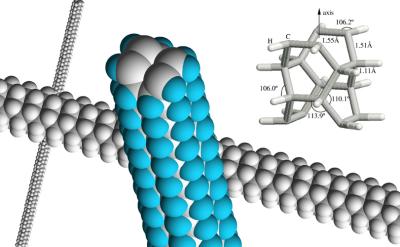
Image

Young Stars in Orion May Solve Mystery of Our Solar System
Scientists Find X-Rays from Stellar Winds That May Play Significant Role in Galactic Evolution

Image
