Physical Sciences
Enzyme Complex Could be Key to New Cancer Treatments
Image

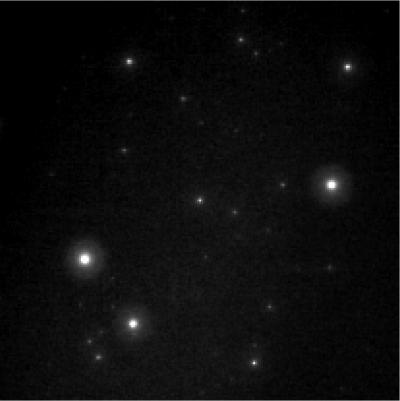
Superbright Explosion is Most Distant Object Ever Visible to the Naked Eye

Image

Scientists See Norwalk Virus' Achilles Heel
Single-Crystal Semiconductor Wire Built into an Optical Fiber
Samarth Earns Faculty Scholar Medal for 2008
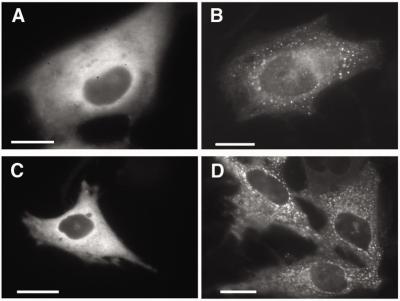
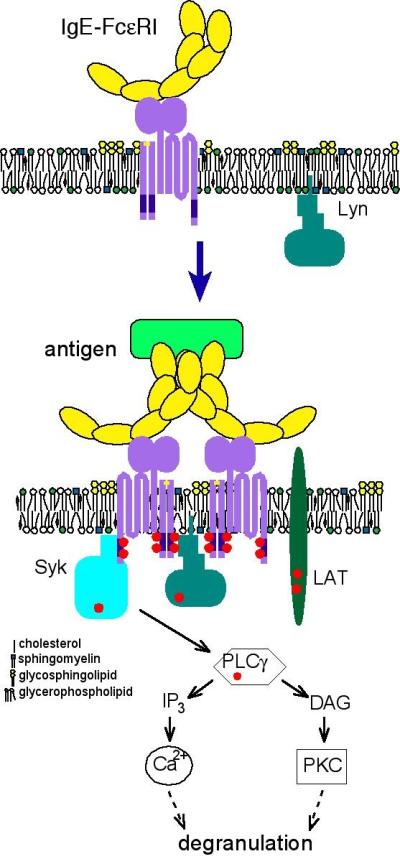
Allergic Response Tied to Lipid Molecules in Cell Membrane
Image

Solar Cell Directly Splits Water for Hydrogen
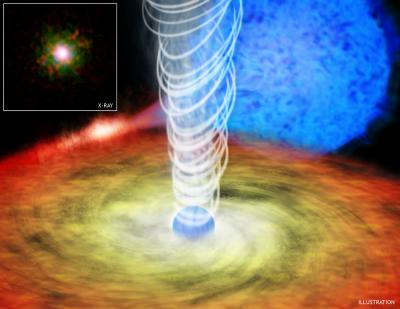
Neutron Stars Join the Black-Hole Jet Set
Image

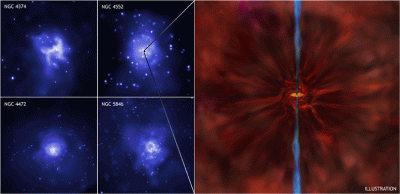
Rapidly Whirling Black Holes Discovered Spinning at Near Maximum Speed
Image

Powerful New Sky Surveys to Explore Dark Energy, Milky Way Galaxy, and Giant Planets

Image
