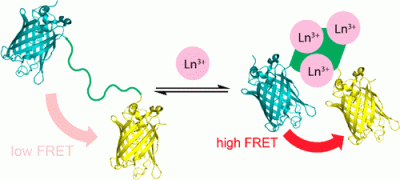
A more efficient and cost-effective way to detect the rare earth metals used in smartphones and other technologies.
LIGO and Virgo Detect Neutron Star Smash-Ups

Image

How the bumble bee got its stripes
NIH grant funds research to pinpoint natural selection’s influence on genomes

Image

Unlocking the mystery behind blood clots
Image

New sensor detects rare metals used in smartphones
Image

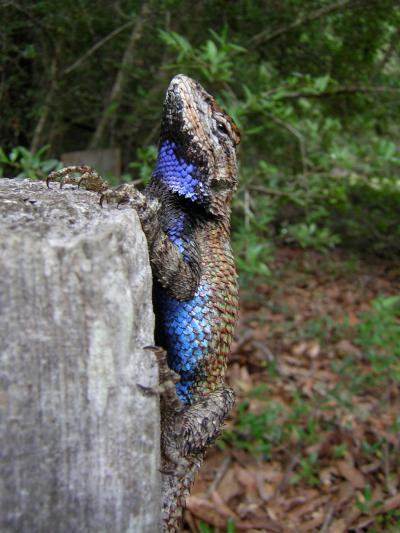
Features that make lizards sexy are resilient to stress

Image

First ever open public alerts from LIGO: Two probable black-hole mergers spotted in first weeks after gravitational-wave detector is updated

Image

A new signal for a neutron star collision discovered

Image

Researchers to study genetic roots of Parkinson's disease with NSF grant
New computer model automatically, aesthetically crops photos