Flies' disease-carrying potential may be greater than thought, researchers say

Image

Experiment Near South Pole Reveals How Earth Blocks High-Energy Particles Produced by Nuclear Reactions

Image

New quest to map stars and galaxies across the entire sky

Image

Sky-high observatory sheds light on origin of excess anti-matter: New study excludes nearby pulsars, points to dark matter as possible culprit

Image

Survival of the least-fit: antiviral drug selectively targets the nastiest viruses
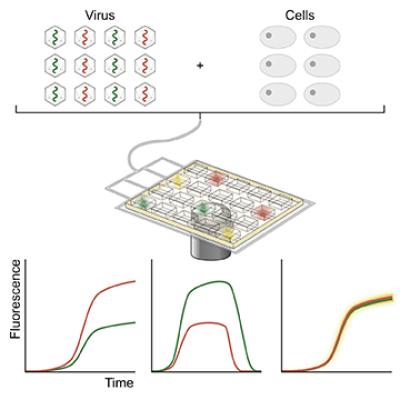
Image

Cryo-electron microscope to bring life sciences and materials sciences together

Image

Mimicking biological process, hydrogel signals and releases proteins
Image

Astronomers discover sunscreen snow falling on hot exoplanet

Image

Identifying the mechanism for a new class of antiviral drugs could hasten their approval
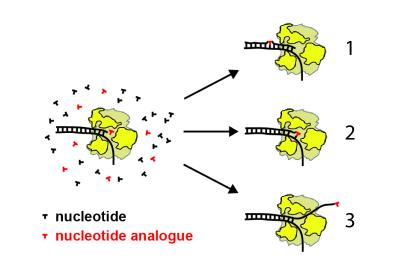
Image

Exploring how herpes simplex virus changes when passed between family members
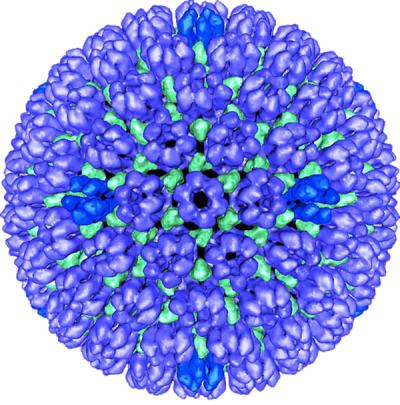
Image
